Elite Iranian Hackers Use AI to Attack Israeli Cyber Experts in Stealth Phishing Blitz
June 25, 2025
Cytela has been monitoring cyber attacks attributed to an Iranian state-sponsored threat group known as Educated Manticore, also tracked as APT42, Charming Kitten, and Mint Sandstorm.
This advanced persistent threat (APT) group is widely believed to operate under the auspices of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), and has a well-documented history of cyber espionage campaigns targeting high-profile individuals.
The current operation, began in mid-June 2025 following the escalation of hostilities between Iran and Israel. The campaign specifically targets Israeli journalists, cybersecurity professionals, and computer science academics, using advanced social engineering techniques to exfiltrate sensitive credentials and bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) protections.
Social Engineering with AI-Enhanced Precision
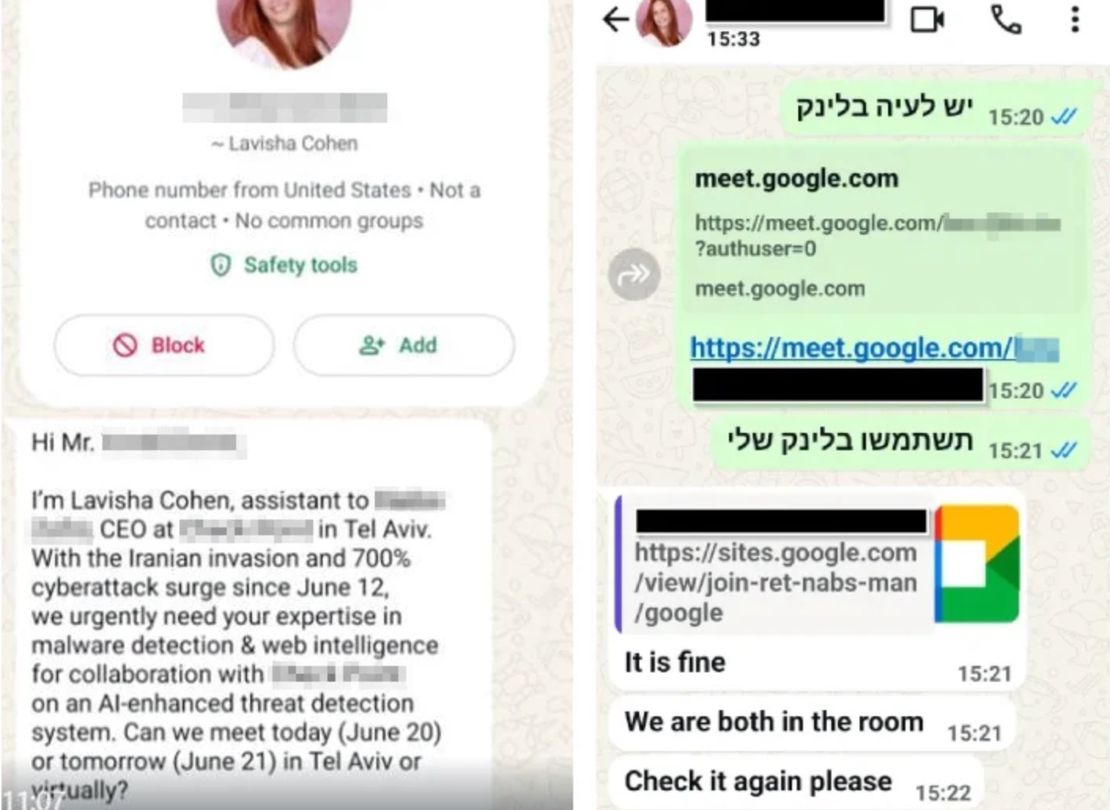
The attackers initiated contact via email and WhatsApp, often posing as assistants to technology executives, cybersecurity firm employees, or researchers. These messages, likely generated or refined using AI tools, exhibit a polished structure and lack grammatical errors, making them highly convincing.
Advanced Phishing Kits and Real-Time Data Exfiltration
The phishing infrastructure used in this campaign demonstrates a high degree of sophistication:
- The fake login pages are built with React-based Single Page Applications (SPA) and feature dynamic routing, closely mimicking legitimate Google services.
- Credential harvesting pages are pre-populated with the victim’s email address, increasing credibility.
- Real-time WebSocket connections are employed to exfiltrate login credentials and 2FA codes instantly.
- A passive keylogger records every keystroke, ensuring even abandoned login attempts may yield valuable data.
In some cases, Google Sites domains are used to host fake meeting pages that visually mirror authentic Google Meet interfaces. These decoys direct unsuspecting victims to malicious pages designed to harvest login credentials and multi-factor authentication tokens—enabling 2FA relay attacks.
Broader Geopolitical Implications
This activity forms part of Iran’s broader cyber operations strategy aimed at gathering intelligence, influencing political dynamics, and undermining adversaries. While the latest campaign has a concentrated focus on Israel, similar tactics have been observed across Europe. Earlier this week, Iranian threat actors reportedly disrupted municipal services in Tirana, Albania, taking down government websites and impairing local infrastructure.
As tensions continue to rise in the Middle East, cybersecurity experts warn that Iranian threat activity is likely to intensify and extend beyond traditional espionage to include attacks on critical infrastructure, supply chains, and technology vendors.
Cytela’s Advisory to Defend Against AI Threats
Cytela recommends organizations remain vigilant and take the following precautions::
- Educate personnel about social engineering tactics and the evolving use of AI-generated phishing content.
- Monitor for suspicious communications, especially from new or unknown contacts claiming to represent reputable organizations.
- Deploy advanced email filtering, endpoint detection, and multi-factor authentication with phishing-resistant tokens.
- Regularly audit account activity and access logs for signs of compromise.